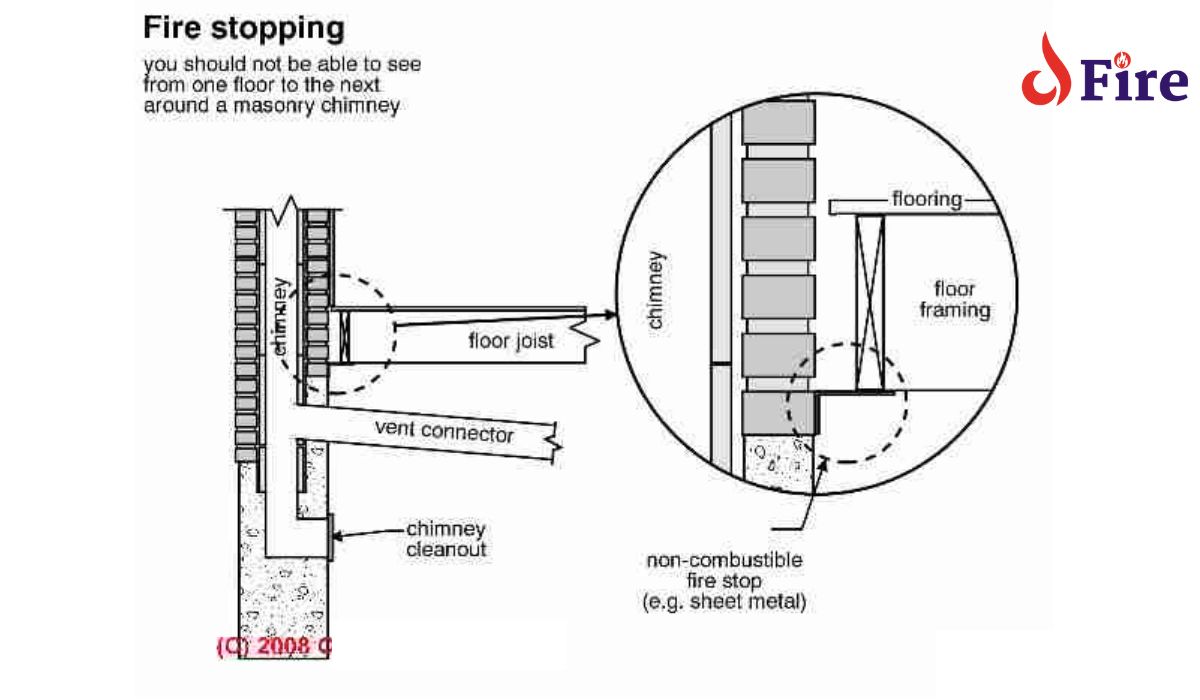
Firestopping is a passive fire protection method used to seal openings and joints in fire-resistance-rated wall or floor assemblies. It helps to prevent the spread of fire and smoke between compartments.
Implementing effective firestopping can greatly enhance a building’s safety by containing fires to their origin, allowing occupants more time to evacuate and reducing damage. This process involves the application of various materials, such as sealants, intumescent products, and firestop pillows, to close off gaps around electrical conduits, pipes, and other penetrations.
Not only does firestopping protect lives and property, but it also ensures that buildings meet strict regulatory compliance for fire safety standards. Ensuring a proper firestop system is integral to the overall fire safety strategy of both new construction and retrofitting projects.
The Mechanics Of Fire Spread
Understanding how a fire spreads throughout a building is crucial. It is the foundation upon which fire safety measures stand. Factors like building design, materials used, and internal configurations can significantly affect this dynamic process. By dissecting the mechanisms at play, we can better prepare and prevent the devastating impact of fires. Let’s delve into the paths a fire takes to travel through buildings and the importance of compartmentalization in halting its progress.
How Fire Travels Through Buildings
Fire moves in predictable patterns. By conquering these patterns, firestopping effectiveness is maximized. Here’s how fire typically travels:
- Conduction: Heat moves through solid materials.
- Convection: Hot gases rise, spreading fire upwards.
- Radiation: Heat radiates, igniting nearby objects.
- Direct Flame: Flames reach new fuel sources.
Building elements like ducts, pipes, and cables can create unintended paths for fire to travel. These are the areas where firestopping tactics are pivotal.
The Role Of Compartmentalization
Compartmentalization is a fire safety strategy. It divides a building into sections using fire-resistant walls and floors. This technique slows down the spread of fire. Here’s why compartmentalization is crucial:
- It contains the fire to its origin point.
- It reduces smoke spread, making evacuation safer.
- It protects escape routes and critical infrastructure.
- It buys time for emergency services to respond.
Firestopping efforts aim to ensure these compartments remain intact. They seal gaps and prevent the passage of flames and smoke. A successful firestopping system can be the difference between a minor incident and a major tragedy.
Firestopping Fundamentals
Understanding the core principles of firestopping is crucial for any building’s safety plan. Effective firestopping can be the difference between minor damage and a major disaster. Let’s dive into the basics of this vital safety measure.
Defining Firestopping
Firestopping is a critical safety feature in modern construction. Its main goal is to contain fires within a small area. By doing so, it limits the spread of fire, smoke, and toxic fumes. This protection saves lives and minimizes property damage.
Materials And Methods
Different situations need specific firestopping solutions. Here are the types of materials and methods commonly used:
- Intumescent materials – Expand when exposed to heat, sealing off gaps.
- Firestop pillows – Easy to install in voids and reconfigurable spaces.
- Sealants and sprays – Provide a flexible barrier to prevent fire spread.
Choosing the right material depends on the building design and compliance with fire safety codes. Professionals select materials that best fit the structure’s specific needs.
Historical Evolution Of Fire Safety
The quest for fire safety has shaped the design and construction of buildings for centuries. As we learned more about fire behavior, societies have continuously improved their methods for containing and preventing fires. This journey is a blend of lessons learned from tragic events and the development of key regulatory measures.
Lessons From Past Fire Disasters
Fire disasters have taught us crucial lessons. Each significant blaze led to better fire safety practices. Let’s revisit some pivotal moments:
- Great Fire of London, 1666: This fire led to the first building codes focusing on fire-resistant materials.
- Chicago Fire, 1871: After this, cities adopted stricter codes for building spacing and fire-resistant construction.
- Triangle Shirtwaist Factory fire, 1911: This disaster prompted laws for fire escapes and factory inspections.
Regulatory Milestones In Building Safety
Fire safety regulations have evolved significantly due to past incidents. We’ve highlighted key milestones in the table below:
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1911 | Introduction of laws for fire escapes and safety inspections. |
| 1930 | Building codes updated to include fire alarms and extinguishers. |
| 1968 | Approval of New York City Building Code for fire safety requirements. |
| 1973 | National Fire Protection Association published Life Safety Code. |
| 2000 | Internationally recognized International Building Code established. |
Firestopping, as part of these developments, is a critical aspect that involves sealing openings to prevent fire spread. It offers another layer of protection, ensuring people can evacuate safely in the event of a fire. As fire safety continues to evolve, firestopping remains a fundamental component of modern building design.

Credit: nefsaindiablog.com
Evaluating The Performance Of Firestopping
Understanding how well firestopping functions is like checking the armor of a superhero. It may look good, but does it do the job when danger strikes? When we talk about firestopping, we discuss its ability to stand against fire. The performance of firestopping is crucial. It ensures our buildings are as safe as they can be. To check its power, we look closely at two things. The fire resistance ratings tell us how long it can fight the fire. Then, testing and certification processes confirm it meets strict safety rules. Let’s dive into what each of these critical checks involves.
Fire Resistance Ratings
Think of fire resistance ratings as a timer for safety. These ratings give a minute-by-minute countdown of how long a firestop can hold a fire at bay. They are usually measured in hours. Fire resistance brings peace of mind, knowing that there is a buffer of time. During this time, people can escape, and firefighters can get to work. Ratings vary based on the design and materials of the firestop. They tell us how effective a firestop will be during an emergency.
Testing And Certification Processes
To make sure firestop products are true heroes, they must pass strict tests. Independent labs set fires to these products in controlled settings. They observe how well the firestop stands its ground. The correct methods and materials make all the difference.
After the test, the firestop can earn a certificate. This proves that it has met the required performance standard. A certified firestop has not just claimed its power against fire. It has proven it. Certificates are like trophies for bravery in the face of fire. They assure us that the firestop will perform its duty well.
Proper Installation Of Firestop Systems
Proper Installation of Firestop Systems is vital for the safety of buildings. Firestopping seals openings to prevent fire, smoke, and toxic gas from spreading. This safety measure is more effective when it is installed correctly.
Best Practices For Contractors
- Understand local codes – Contractors must know and follow all fire code requirements.
- Select correct materials – Match proper firestop materials to each unique situation.
- Train thoroughly – Ensure teams receive proper training on installation techniques.
- Inspect regularly – Check installations frequently to ensure integrity.
- Document everything – Maintain detailed records of materials and placement for accountability.
Common Installation Mistakes
- Misusing materials – Avoid using incorrect firestopping products for specific applications.
- Ignoring gaps – Ensure no gaps remain around penetrations after installation.
- Not sealing properly – Apply materials evenly and thoroughly to prevent leaks.
- Skipping inspections – Regular review of firestop systems is essential to maintain effectiveness.
- Lack of maintenance – Firestop systems need upkeep, especially after building modifications.
Firestop Inspection And Maintenance
Ensuring the safety of a building from fire involves more than just installing firestops. Regular Firestop Inspection and Maintenance form a critical component in maintaining a safe environment. It’s essential to check the integrity of firestops. This process helps to prevent fire, smoke, and gases from spreading during an emergency.
Routine Check-ups For Integrity
Regular inspections are necessary to ensure firestops continue to perform as needed. Trained professionals often carry out these inspections annually. The results confirm whether firestops require repairs or replacements. Building owners should prioritize these inspections. They confirm firestops meet the latest safety standards and regulations.
- Visual evaluation of firestop seals.
- Physical testing for seal durability.
- Documentation of firestop conditions.
Upkeep Challenges In Aging Buildings
Maintaining firestops in older buildings poses unique challenges. The materials used in the past may no longer be sufficient. Aging buildings often require more frequent inspections. It’s vital to replace outdated firestopping systems with modern, code-compliant solutions.
- Identify obsolete materials in firestops.
- Plan upgrades to current safety standards.
- Allocate budget for necessary renovations.
| Firestop Feature | Aging Building | Maintenance Action |
|---|---|---|
| Seal Integrity | Declining | Inspection & Repair |
| Material Compliance | Outdated | Upgrade & Replacement |
| Regulatory Adherence | Non-compliant | Update to Current Codes |
Technological Advancements In Firestopping
Firestopping has witnessed immense growth due to technology. It now offers higher safety levels in buildings. Technological innovations improve its effectiveness and reliability. These advancements provide better protection against the spread of fire and smoke.
Innovations In Firestop Materials
Recent breakthroughs have led to remarkable firestop materials. These include:
- Intumescent products that expand when exposed to heat, sealing off gaps.
- Elastomeric compounds that maintain their integrity under extreme temperatures.
- Firestop collars and wraps for complex pipe configurations.
New compounds are non-toxic and eco-friendly. They ensure safety without harming the environment.
Smart Monitoring Systems
Smart technology transforms firestopping. It now includes:
- Sensors that detect changes in firestop barriers.
- Remote monitoring enables real-time updates on firestop integrity.
These systems integrate with building management systems. They ensure continual protection and swift response during emergencies. This leads to enhanced building safety.
Understanding The Role Of Firestop In Overall Building Safety
Firestopping is a method of sealing buildings to prevent fires. It blocks flames and smoke. It keeps people safe. This system is a key part of building safety.
Integrating Firestopping with Other Fire Protection Systems
Integrating Firestopping With Other Fire Protection Systems
Firestopping works with other systems to protect buildings. It is one piece of fire safety. Fire alarms, sprinklers, and firestopping act together to save lives and property.
- Fire alarms alert people.
- Sprinklers help control fires.
- Firestopping stops fire spread.
They must work together for full safety. If one piece fails, the risk increases.
Firestopping and Occupant Safety
Firestopping And Occupant Safety
Firestopping keeps smoke and flames away from people. Occupant safety is the top priority. It gives people time to escape.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Sealed gaps | Traps fire |
| Safe exit paths | Escape routes stay clear |
Clear signs and lights guide the way out. Firestopping helps maintain these paths. People can leave buildings quickly and safely.
Case Studies: Success And Failure
Exploring Case Studies: Success and Failure in firestopping reveals critical insights. These real-world scenarios highlight the importance of proper firestopping methods. They showcase the drastic difference between success and failure in fire safety.
Analyzing Effective Firestopping Solutions
Understanding successful firestopping begins with analyzing real-life triumphs in fire safety. The implementation of effective firestopping solutions prevents the spread of fire, saving lives and property.
- Case Study 1: A commercial high-rise used intumescent sealants around wiring. The fire was contained to a single floor, limiting damage.
- Case Study 2: A hospital installed firestop collars on plastic pipes. Despite a fire, crucial areas remained safe, allowing safe evacuation.
| Project Type | Firestopping Measures | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Commercial High-Rise | Intumescent Sealants | Fire Contained |
| Hospital | Firestop Collars | Safe Evacuation |
Consequences Of Inadequate Firestopping
Failure to install an appropriate firestopping system can lead to devastating outcomes.
Case Study 3: An industrial complex lacked proper fire barriers. This oversight allowed fire to rapidly spread, causing extensive damage.
Case Study 4: A residential building skipped firestopping in wall penetrations. The fire escalated, resulting in tragic loss.
- Fire Spread Quickly
- Increased Damage and Cost
- Potential Loss of Life
The following table depicts the negative impact of inadequate firestopping:
| Location | Issue | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Complex | No Fire Barriers | Extensive Fire Damage |
| Residential Building | Firestopping Omitted | Loss of Lives |
Looking Ahead: The Future Of Firestopping Technology
The protection against fire remains a top priority in building safety. Firestopping technology is ever-evolving. Innovations aim to enhance protection and safety. The future of firestopping is on a path of advanced development. This advancement aims to adapt to modern architectural complexities.
Predictions And Trends
Emerging trends in firestopping look promising. The focus is on smarter, more effective solutions. Smart materials that respond to heat are in development. They expand to seal off fire paths upon detecting high temperatures. Integration with fire alarms and building management systems is another key trend. This allows for real-time monitoring and faster response during fires. Technologies such as 3D printing might soon create new firestop applications. These could be more tailored to specific building requirements.
- Smarter Firestopping Materials
- Real-time Monitoring Systems
- Customized Solutions via 3D Printing
The Importance Of Continuous Improvement In Fire Safety
Building codes evolve to ensure safety standards rise. Firestopping technology must keep pace. Continuous improvements aim at safeguarding lives and property. Key areas of focus include:
- Enhanced Performance: Better materials to resist fire longer.
- Improved Compliance: Ensuring all firestopping products meet regulatory standards.
- Advanced Installation Techniques: Easier and more reliable ways to install firestopping systems.
The commitment to fire safety progress is clear. Investments in research are ongoing. The aim is to realize the full potential of firestopping. This ensures buildings are safer for everyone.

Credit: fastercapital.com
Frequently Asked Questions On What Is Firestopping
What Is Firestopping In Construction?
Firestopping is a set of systems used in building construction to prevent the spread of fire and smoke through openings and joints in fire-resistance-rated walls and floors.
How Does Firestopping Work?
Firestopping materials seal gaps around electrical conduits, pipes, and ductwork, expanding when exposed to heat to block the passage of fire.
Why Is Firestopping Important?
Firestopping is vital for ensuring building safety by maintaining the integrity of fire-rated compartments, thereby slowing down the spread of fire and smoke.
What Materials Are Used In Firestopping?
Common firestopping materials include intumescent sealants, firestop pillows, mineral wool, and fire-rated caulks designed to resist high temperatures.
Is Firestopping Required By Law?
Yes, firestopping is mandated through building codes and regulations to uphold specific fire safety standards in new construction and renovations.
How Is Firestopping Tested?
Firestopping systems are rigorously tested to meet industry safety standards, typically involving exposure to high temperatures to assess their fire-resistive effectiveness.
Conclusion
Understanding firestopping is crucial for building safety. It seals gaps, preventing fire and smoke spread. Implementing effective firestopping practices saves lives and property. As we’ve discussed, it’s an investment in protection, not just compliance. Remember, diligent maintenance ensures ongoing safety for all occupants.

I’m Abdus Sobur, a highly skilled and professional Fire Safety Officer with a passion for safeguarding lives and property. Over the course of my career, I’ve conducted numerous successful fire safety audits, earning a reputation for excellence in ensuring public safety.
In addition to my role as a Fire Safety Officer, I’m also dedicated to raising awareness about the importance of fire safety. Through my blog, I share insights into the functions of different fire safety equipment, aiming to empower individuals with the knowledge they need to protect themselves and their communities.
I’m driven by a deep commitment to promoting fire safety awareness and preventing fire-related incidents.