Fire hydrant detail involves the specific design, placement, and maintenance of fire hydrants for effective fire suppression. Proper fire hydrant detail ensures quick access to water during emergencies.
Fire hydrants are critical components of urban safety infrastructure. They provide firefighters with immediate access to water in the event of a fire. Proper placement and maintenance of fire hydrants are crucial for optimal performance. Factors such as location, pressure, and accessibility must be carefully considered.
Regular inspections ensure hydrants remain operational and free from obstructions. Accurate documentation of fire hydrant details aids in efficient emergency response. Fire hydrants must comply with local regulations and standards to guarantee effectiveness. Ensuring these elements are in place can significantly enhance community safety and fire response efficiency.
Importance Of Fire Hydrants
Fire hydrants are crucial for urban safety and emergency response. These devices supply water to firefighters quickly. Their presence can save lives and properties during a fire.
Urban Safety Role
Fire hydrants play a vital role in urban areas. They ensure the quick availability of water during fires. This rapid access helps control fires before they spread.
- Quick water access saves lives.
- Helps in limiting fire damage.
- Ensures safety of buildings and people.
Emergency Response Enhancement
Fire hydrants enhance the efficiency of emergency responses. They provide a reliable water source for firefighters. This helps in extinguishing fires more effectively.
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Reliable water source | Faster fire control |
| Easy access | Improved response times |
| Strategic placement | Enhanced urban safety |
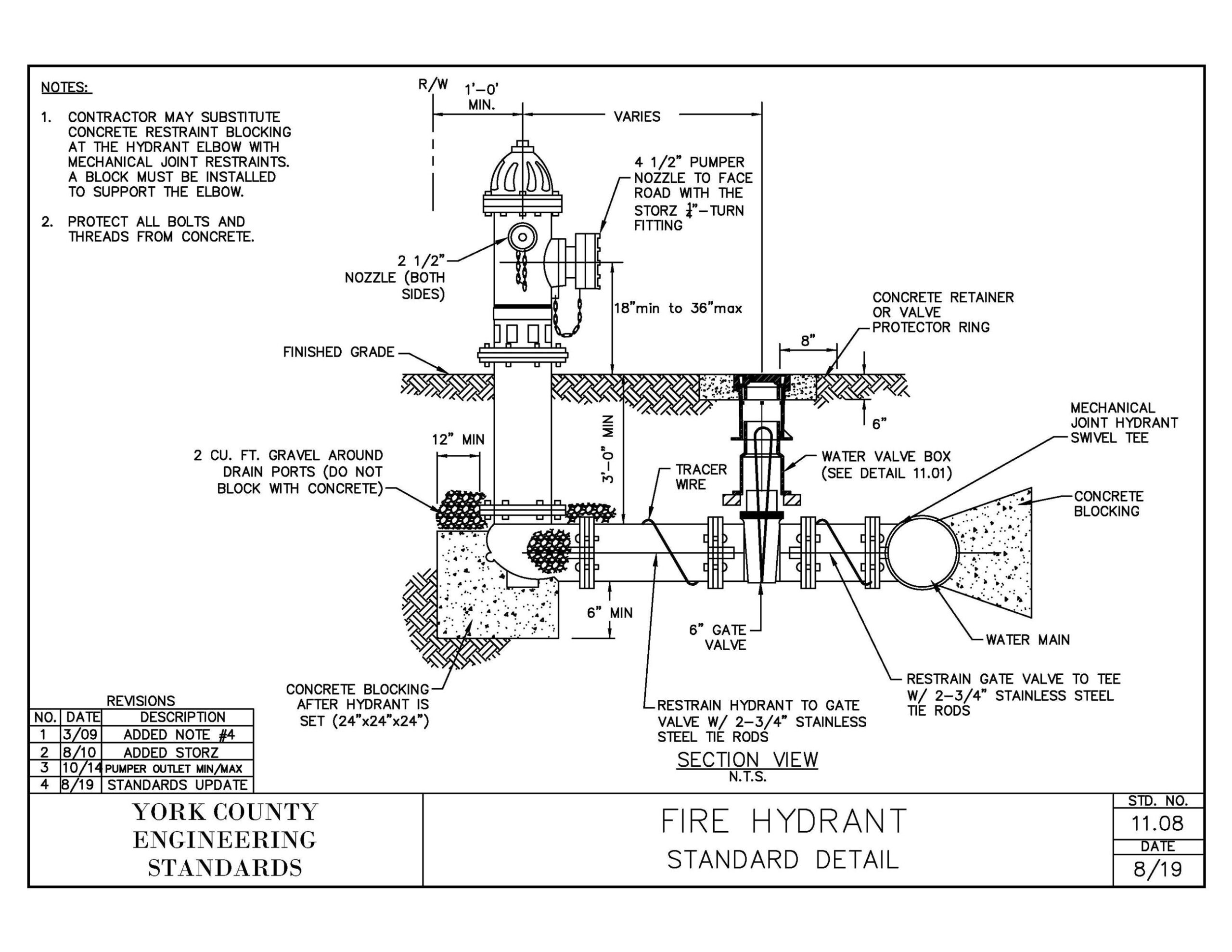
Types Of Fire Hydrants
Fire hydrants are crucial in firefighting. They provide easy access to water. Knowing the different types helps in emergencies. This section covers two main types: Wet Barrel Hydrants and Dry Barrel Hydrants.
Wet Barrel Hydrants
Wet barrel hydrants are filled with water. They have water in their barrels at all times. These hydrants are common in warm climates. Here’s what you need to know:
- Water-filled barrel
- Easy to use in emergencies
- Quick water access
- Not suitable for cold climates
Wet barrel hydrants have separate valves for each outlet. This design allows easy control. Firefighters can open one or multiple outlets. It makes firefighting more efficient.
Dry Barrel Hydrants
Dry barrel hydrants are empty until needed. These hydrants are designed for cold climates. They prevent water from freezing inside. Here are key features:
- Empty barrel until use
- Best for freezing conditions
- Prevents water freezing
- Requires proper maintenance
Dry barrel hydrants have a main valve at the base. The valve keeps water below ground level. This design ensures water doesn’t freeze. Opening the hydrant lets water flow up.
| Feature | Wet Barrel Hydrant | Dry Barrel Hydrant |
|---|---|---|
| Water in Barrel | Always | Only when in use |
| Climate Suitability | Warm | Cold |
| Main Valve Location | At each outlet | Below ground |
Both types serve their purposes well. Choosing the right one depends on your local climate. Maintaining them ensures they work in an emergency.
Hydrant Design And Construction
Fire hydrants play a crucial role in firefighting efforts. Hydrant design and construction ensure these devices are reliable and efficient. They must withstand harsh conditions and provide quick access to water. The following sections delve into the materials and structural features of fire hydrants.
Materials Used
Fire hydrants are made from strong and durable materials. The main materials include cast iron, ductile iron, and bronze. Cast iron is known for its strength and durability. Ductile iron adds flexibility, reducing the risk of cracks. Bronze is used for internal parts to resist corrosion.
| Material | Properties |
|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Strength, Durability |
| Ductile Iron | Flexibility, Crack Resistance |
| Bronze | Corrosion Resistance |
Structural Features
Fire hydrants have several important structural features. These features ensure easy access and operation. The main components include the bonnet, stem, and outlet nozzles. Each part plays a vital role in the hydrant’s functionality.
The bonnet covers the top and houses the operating mechanism. The stem connects the bonnet to the valve. The outlet nozzles provide multiple connections for hoses. These features make hydrants efficient and reliable.
- Bonnet – Covers the top, houses the mechanism.
- Stem – Connects bonnet to valve.
- Outlet Nozzles – Multiple connections for hoses.
Understanding these materials and features helps in maintaining and operating fire hydrants. Reliable hydrants ensure quick access to water during emergencies. Proper design and construction are essential for their effectiveness.
Credit: www.wheaton.il.us
Installation Considerations
Proper installation of fire hydrants is crucial for effective fire response. This section covers important considerations for placing and making fire hydrants accessible. Ensuring correct installation enhances safety and operational efficiency.
Location Placement
Fire hydrants must be placed strategically for quick access. Consider placing hydrants at street intersections. This allows fire trucks to reach them easily. Avoid placing hydrants behind obstacles like trees or fences.
Follow local regulations for hydrant placement. Typically, hydrants should be within 300 feet of buildings. Ensure hydrants are visible from the street. Visibility is key for quick identification during emergencies.
Accessibility Requirements
Accessibility is crucial for effective fire hydrant use. Ensure hydrants have a clear path around them. This path should be at least 3 feet wide. Remove any obstructions like parked cars or debris.
Regular maintenance is important to keep hydrants accessible. Conduct checks to ensure valves are operational. Make sure the hydrant is not buried by snow or dirt. Accessibility ensures fire responders can connect hoses quickly.
| Requirement | Details |
|---|---|
| Clear Path | At least 3 feet wide |
| Visibility | Visible from the street |
| Distance from Buildings | Within 300 feet |
Follow these installation considerations to ensure efficient fire hydrant performance. Proper placement and accessibility are key to safety.
Maintenance And Inspection
Proper maintenance and inspection of fire hydrants are crucial. It ensures they function well in emergencies. Regular checks help identify potential issues early. This section will discuss the key aspects of maintaining and inspecting fire hydrants.
Routine Checks
Routine checks are essential for fire hydrant upkeep. These checks should be done at least twice a year. Here is a list of tasks to include in routine checks:
- Check for visible damage or leaks.
- Ensure the hydrant is easily accessible.
- Test the water pressure and flow rate.
- Inspect the caps and valves for proper function.
- Lubricate the stem and cap threads.
Routine checks can prevent many common issues. They ensure the hydrant is always ready for use.
Common Issues
During maintenance, you may encounter some common issues. Here are some of the most frequent problems:
| Issue | Description |
|---|---|
| Leaks | Leaks can occur at the base or nozzle. |
| Corrosion | Corrosion weakens the hydrant and can cause failure. |
| Obstructions | Debris or ice can block the hydrant. |
| Valve Issues | Valves may become stuck or hard to turn. |
Address these issues promptly to ensure hydrant reliability. Regular maintenance helps keep these problems at bay.

Credit: codelibrary.amlegal.com
Hydrant Operation
Fire hydrants are crucial in firefighting. Understanding their operation ensures safety and efficiency. This section will explain the proper usage and handling emergencies.
Proper Usage
Proper usage of a fire hydrant is essential. Ensure the hydrant is fully opened. Partial opening can cause water pressure issues. Follow these steps for correct usage:
- Use the correct hydrant wrench.
- Turn the wrench counterclockwise to open.
- Open the hydrant fully to avoid pressure problems.
- Check for leaks around the base.
Always wear protective gear when operating a hydrant. Safety is the top priority.
Handling Emergencies
During emergencies, quick and efficient hydrant operation is vital. Follow these steps to handle emergencies effectively:
- Stay calm and assess the situation.
- Locate the nearest hydrant quickly.
- Clear any obstructions around the hydrant.
- Open the hydrant fully using the proper technique.
- Ensure a stable water flow to the fire hoses.
Communication with the firefighting team is crucial. Relay any issues immediately.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Stay calm and assess the situation. |
| 2 | Locate the nearest hydrant quickly. |
| 3 | Clear any obstructions around the hydrant. |
| 4 | Open the hydrant fully using the proper technique. |
| 5 | Ensure a stable water flow to the fire hoses. |
Always report any damage or issues with the hydrant after use. Maintenance is key to functionality.
Legal And Regulatory Aspects
Understanding the legal and regulatory aspects of fire hydrant detail is essential. Compliance ensures safety and avoids penalties. This section explores compliance standards and inspection protocols.
Compliance Standards
Fire hydrants must meet specific compliance standards. These standards are set by local, state, and federal authorities. Hydrants need to be accessible and functional at all times. They must be visible and free from obstructions.
- Local Fire Codes
- National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) guidelines
- American Water Works Association (AWWA) standards
Adhering to these standards prevents legal issues. It also ensures the hydrants work during emergencies.
Inspection Protocols
Regular inspections are crucial for fire hydrant maintenance. Inspections ensure hydrants are in working order. They also help identify potential problems early.
- Visual Inspection: Check for damage or leaks.
- Operational Test: Ensure the hydrant opens and closes properly.
- Pressure Test: Measure water pressure to confirm adequate flow.
Inspections should be documented. Records must include the date, time, and inspector’s name. This documentation is vital for accountability and legal compliance.
| Inspection Type | Frequency | Key Points |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Monthly | Check for visible damage and obstructions |
| Operational Test | Quarterly | Ensure proper opening and closing |
| Pressure Test | Annually | Measure water pressure and flow |
Technological Advancements
Fire hydrants have evolved with technology. These advancements ensure better safety and efficiency. Let’s explore the latest innovations in fire hydrant technology.
Smart Hydrants
Smart hydrants are revolutionizing firefighting. These devices provide real-time data. They can detect leaks, measure water pressure, and monitor usage. This information helps in quick decision-making during emergencies.
Smart hydrants use IoT (Internet of Things) technology. They connect to central systems. This allows firefighters to access data remotely. Smart hydrants improve response times and reduce water wastage.
Data Integration
Data integration is crucial for modern fire hydrants. By integrating data, cities can optimize their water resources. This integration includes:
- Water pressure levels
- Leak detection
- Maintenance schedules
Integrated data helps in predictive maintenance. It reduces the chances of hydrant failures. This ensures hydrants are always ready for use.
Fire departments can access this data through dashboards. These dashboards provide a clear overview of the hydrant network. This information is vital for efficient firefighting.
Below is a table summarizing the benefits of data integration:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Efficiency | Optimizes resource allocation |
| Predictive Maintenance | Reduces unexpected failures |
| Real-Time Monitoring | Improves response times |
Technological advancements in fire hydrants enhance public safety. They ensure efficient use of resources and quick response during emergencies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Fire Hydrant Markings?
Fire hydrant markings indicate water flow rate, hydrant type, and operational status. Common colors include red, yellow, blue, and green.
What Are The Standards For Fire Hydrants?
Fire hydrants must follow NFPA 291 standards. They should be color-coded for visibility and flow rate identification. Installation must meet local regulations. Regular maintenance is essential for functionality.
What Are The Parts Of Fire Hydrant?
A fire hydrant consists of several parts: the bonnet, operating nut, upper barrel, lower barrel, valve, and hose outlets.
How Much Clearance Is Needed Around A Fire Hydrant?
A fire hydrant needs 3 feet of clearance on all sides. This ensures easy access for emergency responders. Maintain this space to comply with safety regulations.
Conclusion
Understanding fire hydrant details is crucial for safety and efficiency. Proper maintenance ensures readiness in emergencies. Equip your community with this knowledge to enhance safety protocols. Stay informed and proactive about fire hydrant management. Your vigilance could save lives and protect property.
Prioritize safety and invest in regular inspections.

I’m Abdus Sobur, a highly skilled and professional Fire Safety Officer with a passion for safeguarding lives and property. Over the course of my career, I’ve conducted numerous successful fire safety audits, earning a reputation for excellence in ensuring public safety.
In addition to my role as a Fire Safety Officer, I’m also dedicated to raising awareness about the importance of fire safety. Through my blog, I share insights into the functions of different fire safety equipment, aiming to empower individuals with the knowledge they need to protect themselves and their communities.
I’m driven by a deep commitment to promoting fire safety awareness and preventing fire-related incidents.

